
Weight loss surgery, or bariatric surgery, is a medical procedure designed to aid significant weight loss by modifying the digestive system, particularly for individuals with a BMI of 40 or above, or 35-39.9 when accompanied by serious health concerns. Common types include gastric sleeve, gastric bypass, and adjustable gastric banding, each with unique mechanisms. Postoperative care is crucial for success and includes dietary changes, nutritional supplements, and ongoing healthcare support to prevent complications like nutrient deficiencies and digestive issues.
Getting help with weight loss through weight loss surgery (Bariatric surgery)
Weight loss surgery, also called bariatric surgery, involves changing the digestive system to help people lose weight and reduce the risk of weight-related health issues like heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. For many, diet and exercise alone aren’t enough to achieve sustained weight loss. Metabolic and bariatric surgery comes into play when these methods have failed or when significant health problems arise due to excess weight.
Who is a candidate for weight loss surgery
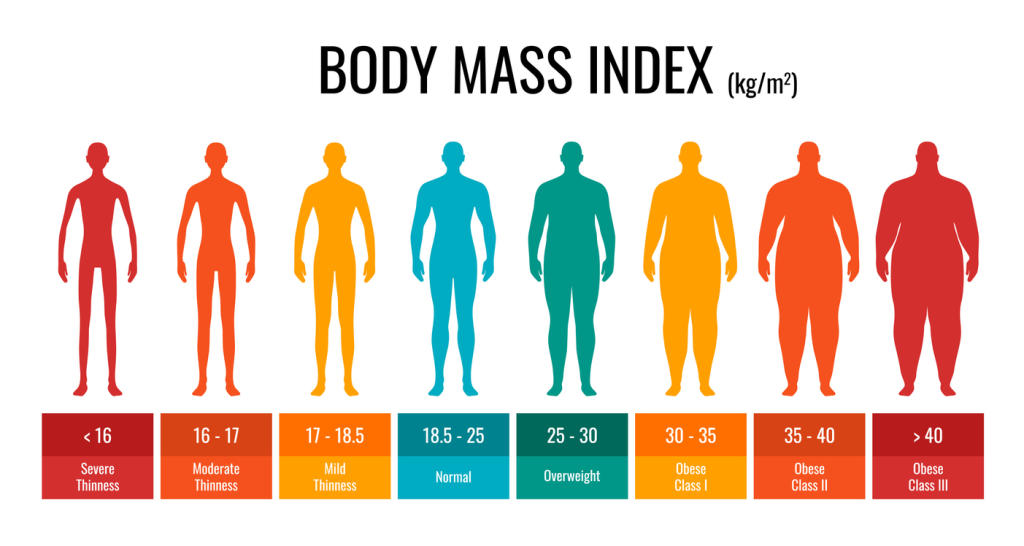
A candidate for weight loss surgery typically undergoes a thorough evaluation process to determine their suitability for the procedure. This assessment begins with calculating the individual’s Body Mass Index (BMI), which serves as a primary indicator of obesity.
Eligability based on BMI
- BMI of 35 or above
- BMI of 30 or above and at least one illness such as:
- Diabetes
- Back pain
- Sleep apnoea
- Joint problems
- At least 6 months of alternative weight loss options that have failed
Adolescents are eligible for the gastric sleeve procedure if they meet the following conditions:
- BMI of 35 or more and any obesity-related illness
- BMI of 30 or more with a severe obesity-related illness
Beyond BMI, healthcare professionals consider a candidate’s overall health, previous weight loss attempts, and commitment to lifestyle changes post-surgery. Psychological evaluations may also be conducted to ensure candidates have the necessary support and resilience to navigate the emotional challenges associated with significant weight loss. Ultimately, the decision to proceed with surgery rests on a collaborative discussion between the candidate and their medical team, focusing on achieving the best possible long-term outcomes.
Join Our Free Weight Tracker Today!
Easily track your weight and measurements, and visualize your progress with charts and photos. Sign up for personalized support from our expert team! Start your journey now!
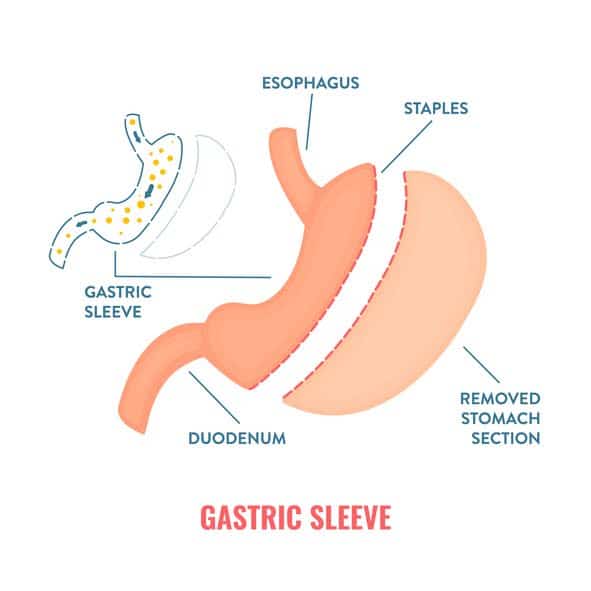
Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, involves:
- Removing a significant portion of the stomach
- Leaving a tube-like “sleeve” that can hold about 200ml of food
- Typically done laparoscopically, with small instruments inserted through tiny incisions in the upper abdomen
- Stapling the stomach vertically during the surgery
- Removing the larger, curved part of the stomach
The result is a smaller stomach that not only limits food intake but also induces hormonal changes that help with weight loss and alleviate conditions such as high blood pressure and heart disease. Patients can expect the surgery to last one to two hours, with a hospital stay of one to two nights. The reduced stomach capacity helps patients feel full sooner and stay satisfied longer, promoting sustained weight loss.
Gastric sleeve surgery is a favored option for its efficiency and relatively uncomplicated procedure. Yet, keep in mind that it necessitates a dedication to enduring lifestyle modifications to uphold weight loss and overall health.
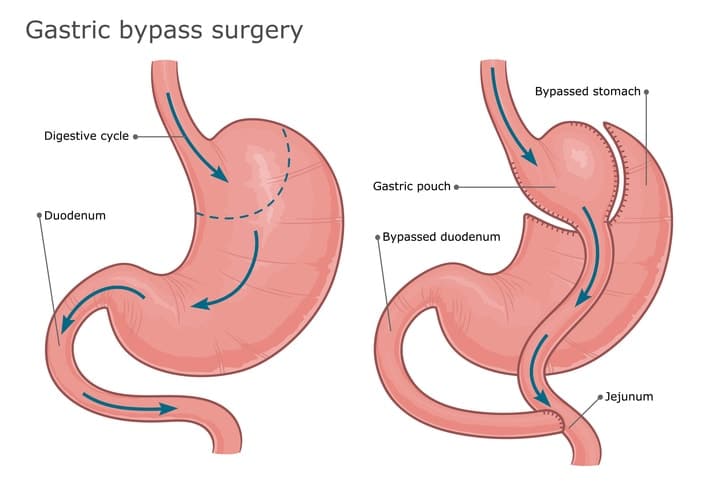
Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery, often referred to as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is another common weight loss surgery. This procedure involves creating a small stomach pouch about the size of an egg, which holds roughly one cup of food. This pouch is then attached directly to the lower part of the small intestine, bypassing most of the stomach and the first part of the small intestine, leading to fewer calorie absorptions and significant weight loss.
The surgery can be performed laparoscopically or as an open procedure, depending on the patient’s situation and the surgeon’s recommendation. One potential risk of gastric bypass surgery is dumping syndrome, where food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, causing symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and cramps.
Although there are inherent risks, gastric bypass surgery proves highly effective in assisting patients with weight loss and the management of obesity-related conditions. The significant reduction in calorie and nutrient absorption contributes to rapid and substantial weight loss, making it a preferred option for many individuals struggling with severe obesity.
Adjustable Gastric Banding
This type of weight loss surgery is now considered outdated, and only a few bariatric surgeons still perform it.
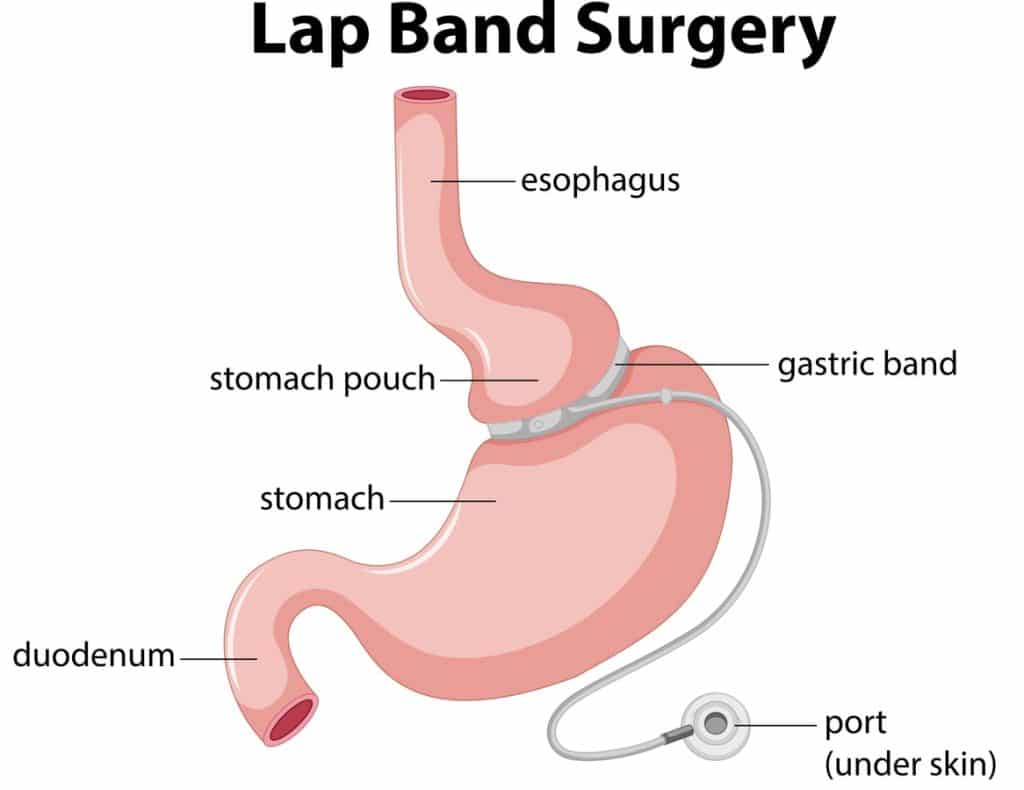
Adjustable gastric banding, or lap band surgery, involves:
- Placing a gastric band around the top of the stomach to create a small pouch
- Limiting the amount of food the stomach can hold
- Promoting weight loss by making the patient feel full sooner and with less food
- Performing the surgery laparoscopically, using small incisions in the upper abdomen.
Post-surgery, the band can be adjusted by injecting or removing fluid from a balloon around the band via a port under the skin. This allows for personalized adjustments to control the rate of weight loss and manage any discomfort. However, adjustable gastric banding is associated with more complications and less weight loss compared to other bariatric surgery procedures, making it a less common choice.
Candidates for this procedure typically have a BMI over 40 or a BMI between 35 and 40 with conditions like sleep apnea or type 2 diabetes. Despite its challenges, adjustable gastric banding offers a reversible and adjustable option for weight loss surgery.
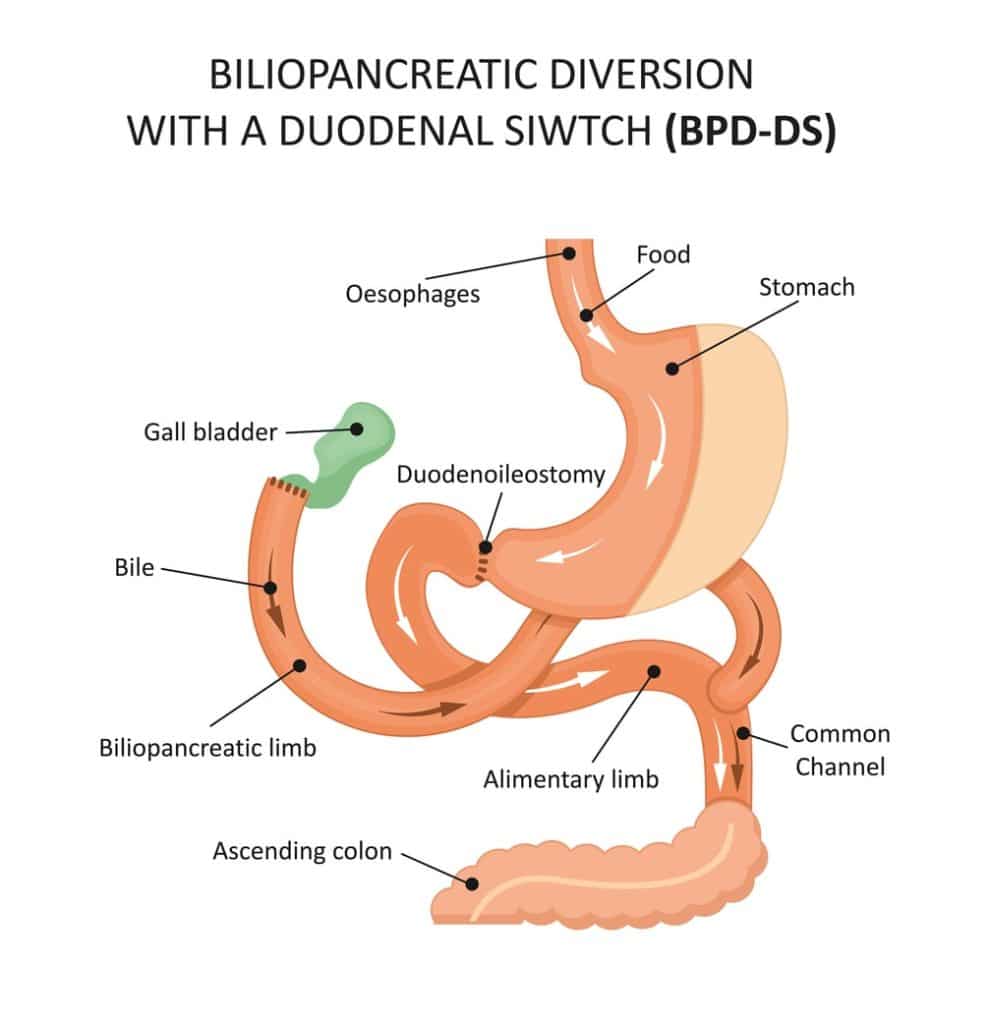
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) is a two-part surgery that combines a gastric sleeve procedure with an intestinal bypass to significantly reduce calorie absorption and promote substantial weight loss. The first part involves removing about 80% of the stomach, leaving a tube-shaped stomach.
The second part connects the remaining stomach to a much shorter section of the small intestine, bypassing a large portion of it. This drastic reduction in the small intestine’s length limits the body’s ability to absorb calories and nutrients, leading to significant weight loss. BPD/DS is generally recommended for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 50 due to its effectiveness.
The procedure can be executed in two phases: the sleeve gastrectomy first and the intestinal bypass later. Although it provides the most substantial weight loss among bariatric surgeries, it comes with elevated risks and demands rigid compliance with nutritional guidelines after the surgery.
Other Weight Loss Surgeries
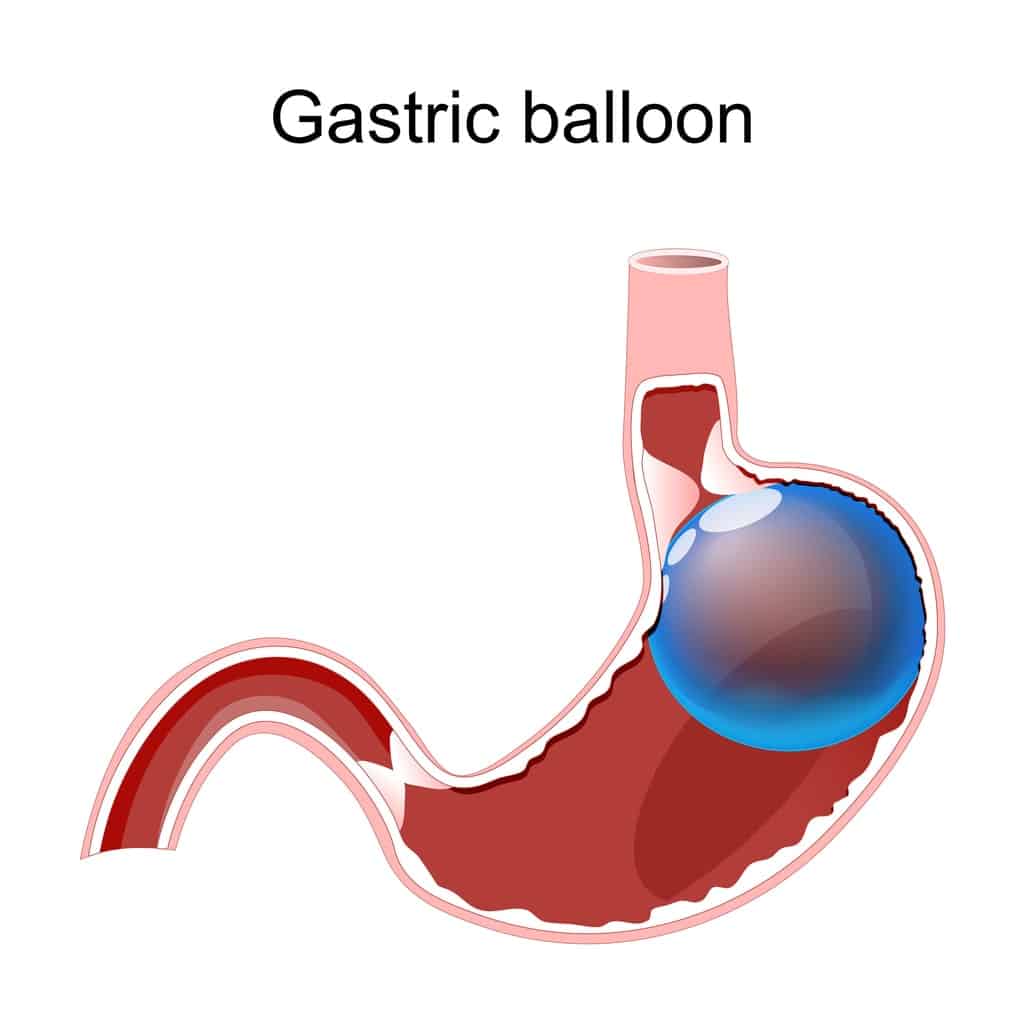
Among other weight loss surgeries, the gastric balloon procedure stands out for its minimally invasive nature. This involves placing a deflated balloon into the stomach using an endoscope, which is then filled with saline to reduce stomach volume. Candidates for this procedure usually have a BMI of 30 to 40 and have not succeeded in losing weight through diet and lifestyle changes.
The insertion of the gastric balloon is an outpatient procedure taking about 15 to 20 minutes. Once in place, the balloon helps patients feel full with less food, aiding gradual weight loss of 10 to 15% of body weight within six months. Although less permanent than other weight loss surgeries, the gastric balloon offers a viable option for those looking to kickstart their weight loss journey with fewer risks.
How to Prepare for Weight Loss Surgery
Getting ready for weight loss surgery necessitates various steps to secure the best possible outcomes and minimize risks. Patients undergo bloodwork and other medical tests to check their metabolic and nutritional status. Pre-surgery evaluations include consultations with various healthcare professionals, such as an internist, dietitian, psychiatrist or psychologist, and bariatric surgeon.
Lifestyle changes are also crucial. Patients are advised to:
- Quit smoking well in advance of the surgery, as smoking increases the risk of complications.
- ** sleep habits and manage stress.
- Adopt a healthy eating plan and become more active.
- Meet with a registered dietitian to learn about the necessary dietary changes before and after surgery.
Ensuring insurance coverage and gathering the required documentation is another important step. Additionally, discussing realistic expectations with a healthcare provider and considering mental health support can help patients prepare for the significant lifestyle changes post-surgery.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Postoperative care and recovery follow a regulated diet progression, which begins with sugar-free, non-carbonated liquids in the initial week, transitioning to pureed foods for the subsequent three weeks, and finally easing into regular foods after roughly a month. Patients are encouraged to eat small meals and chew their food well to aid digestion.
Nutritional supplements are essential to prevent deficiencies. Patients must take a bariatric-specific multivitamin, calcium, and vitamin D3 supplements daily. Long-term follow-up plans, including regular visits to the surgeon and primary care provider, are crucial to monitor nutrition and lifestyle modifications. Physical activity is equally important, with recommendations to engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise daily.
Avoiding NSAIDs is advised to reduce the risk of gastric and marginal ulcers. Women are advised to use effective birth control methods for the first 12 to 18 months post-surgery to ensure proper nutritional status. Remember to follow these guidelines to ensure a smooth recovery and long-term weight loss..
Potential Risks and Complications
Weight loss surgery is associated with diverse risks and potential complications. Common risks include:
- Acid reflux
- Anesthesia-related issues
- Chronic nausea and vomiting
- Infection
- Obstruction of the stomach
These complications can occur post-surgery.
Long-term complications of digestive and kidney diseases may include:
- Malnutrition
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Bowel obstructions
- Ulcers
- Hernias
Patients must comply with lifelong micronutrient supplementation to prevent deficiencies. Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor levels of iron, B12, and vitamin D.
Specific risks associated with different surgeries include dumping syndrome after gastric bypass and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch, which can cause symptoms like nausea and dizziness. Adhering to postoperative guidelines and maintaining close follow-up with healthcare providers can help mitigate these risks.
Expected Weight Loss Results
Patients can anticipate shedding 60 to 80 percent of their excess body weight within a year to year and a half after weight loss surgery, contingent on the type of procedure and personal factors. For instance, those undergoing BPD/DS can lose approximately 70-80% of their excess weight within two years. Factors influencing weight loss include the type of surgery, patient compliance with dietary and lifestyle changes, and gender differences. Successful outcomes are typically defined as achieving 50-70% excess weight loss or 20-30% total body weight loss. It’s important to note that it can take one to two years to reach the lowest weight, with some individuals experiencing weight regain starting around three years post-surgery.
Maintaining weight loss requires ongoing commitment to lifestyle changes and regular follow-up with healthcare providers. This helps ensure that the initial ** weight loss transitions into sustained, long-term success.
Long-Term Lifestyle Changes
Securing long-term success post-bariatric surgery necessitates a commitment to enduring lifestyle modifications. Patients need to adopt new eating habits, such as consuming small, well-chewed meals and taking prescribed dietary supplements. Regular exercise is also crucial, with recommendations to engage in 30 to 45 minutes of aerobic exercise three to five times a week.
Follow-up plans play a vital role in monitoring nutrition and health conditions. Regular visits to dietitians, psychologists, and other health professionals can help patients stay on track. Joining support groups provides additional motivation and support, helping patients maintain a healthy weight and ** any physical or emotional challenges.
Adhering to these long-term lifestyle changes not only supports sustained weight loss but also ** overall physical and emotional health, reducing the risk of weight-related health problems like heart disease and high blood pressure.
Summary
Weight loss surgery offers a ** path for individuals struggling with severe obesity and related health issues. From gastric sleeve and gastric bypass surgeries to adjustable gastric banding and BPD/DS, each procedure has its unique benefits and considerations. Preparing for surgery, understanding postoperative care, and committing to long-term lifestyle changes are crucial for success.
By collaborating closely with healthcare professionals and making informed decisions, patients can achieve substantial weight loss and enhance their overall health and quality of life. The journey may be challenging, but the rewards of a **, more vibrant life are well worth the effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
People with a BMI of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 30-39.9 with serious weight-related health issues are candidates for weight loss surgery.
Gastric sleeve surgery is a procedure that removes a large part of the stomach to create a smaller, tube-like stomach, reducing its capacity and promoting hormonal changes that aid in weight loss.
Gastric bypass surgery carries risks such as dumping syndrome, bowel obstruction, ulcers, hernias, and long-term complications like malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies. Be sure to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider.
After bariatric surgery, patients can expect to lose 60 to 80 percent of their excess body weight within 12 to 18 months, varying based on surgery type and individual factors.
After weight loss surgery, it’s crucial to make long-term changes in eating habits, exercise regularly, and follow up with healthcare professionals for sustained weight loss and overall health.