Treating Loose Skin Following Bariatric Surgery on the Abdomen and Back
Treating loose skin on the abdomen and back following bariatric surgery involves non-invasive approaches like maintaining a balanced diet, exercising, and topical treatments; or surgical procedures like an abdominoplasty.
Abdominal and back skin can lead to health and psychological complications. Therefore, most post-bariatric patients will seek ways to get rid of the excessive loose skin on their back and abdomen. Treating loose skin resulting from bariatric surgery involves non-surgical or surgical approaches.
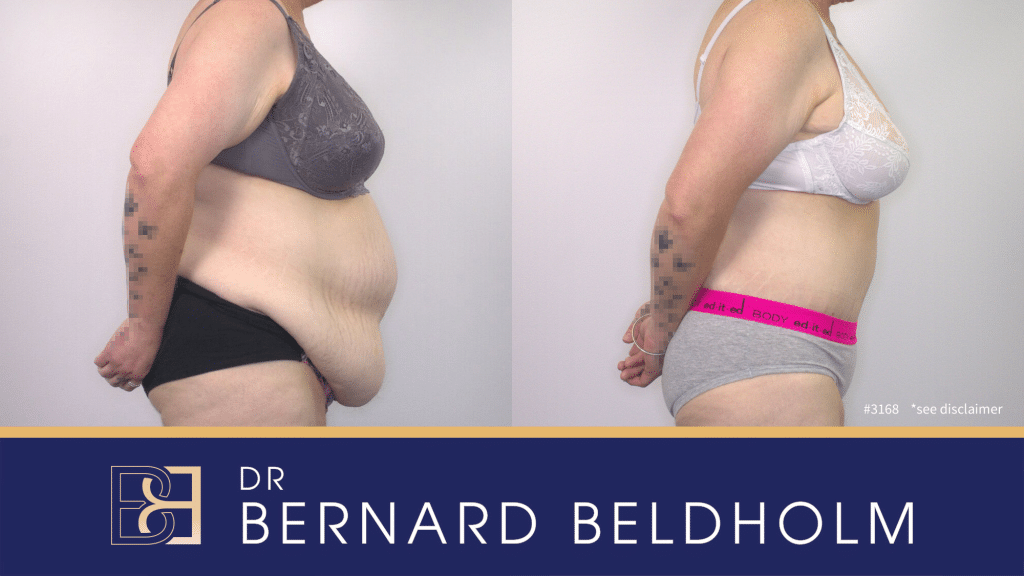
Tattoo (on right arm) blurred for privacy
Disclaimer: Operation performed by Dr Bernard Beldholm. Adult content, surgery has risks; individual results vary, seek 2nd opinion. Please see the full disclaimer.
Factors Affecting Skin Tightening After Bariatric Surgery
There are several factors that influence how the skin tightens and bounces back after bariatric surgery. These include:
Age
The skin loses elasticity with age, resulting in more redundant skin after bariatric surgery in older patients. Skin elasticity determines how the skin bounces back after stretching. Loss in skin elasticity results from low production of elastin and collagen.
Genetics
Genetics is a key determinant of most conditions in our bodies. Some people are predisposed to less skin elasticity, making them more likely to have strecthy skin after bariatric surgery.
Amount of Weight Lost
Patients who lose a large amount of weight, 50kg (approximately 100 pounds) or more, are more likely to experience loose skin. In addition, losing weight within a short period increases the chance of loose skin because the skin has less time to retract normally.
According to a study on post-bariatric surgery, “[t]he sudden change in body mass index (BMI) after weight loss lowers skin tone and leads to a failure of the excess soft tissue to retract, resulting in redundant skin.”
Another study shows that “[p]atients with a weight loss >50 kg showed a significantly redundant skin discomfort compared to weight loss <20 kg.”
Certain Medical Conditions That Cause Skin Thinning
Some patients suffer from medical conditions that affect the skin’s elasticity. These include illnesses that impair collagen production, leading to skin thinning. These include subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma and Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum, among other medical conditions.
Smoking
Smoking causes premature ageing, leading to the production of less collagen and elastin. This results in skin thinning and loss of skin elasticity.
Treatment Options: Common Non-Invasive Approaches
There are various treatment options for loose skin following bariatric surgery. Non-invasive ones include:
Healthy Diet, Exercise, and Hydration
Post-bariatric patients are advised to maintain a healthy diet to ensure wound healing. Patients should avoid unhealthy eating habits like taking too much food at a time, and are encouraged to chew food well.
Patients should also ensure they stay hydrated by consuming lots of fluids to keep the skin supple. In addition, patients are advised to exercise regularly to help build muscle.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments, like creams and massages, help moisturise the skin and promote the production of elastin and collagen, enhancing its elasticity. However, there is no evidence to support their effectiveness.
Compression Garments
Compression garments apply pressure on the skin, offering support and promoting lymphatic drainage. They provide a short-term solution by reducing the appearance of loose skin.
Vitamin and Mineral Supplements
Vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin B12, Vitamin C, and iron, help promote skin healing and offer the nutrients required to ensure strong and elastic skin during your weight loss journey.
A study on post-bariatric surgery published in Pubmed suggests that “[p]atients who underwent bariatric surgery are at risk of nutrient deficiencies, including vitamins B12, B1, folate, A, D, C, and K, as well as trace minerals, such as iron, zinc, selenium, and copper.”
Non-Invasive Procedures
Cryotherapy and laser treatment help stimulate collagen production, the skin’s strength and elasticity; however, they have minimal effect on significant loose skin.
Surgical Procedures to Treat loose Skin Following Bariatric Surgery
Non-invasive treatment options offer a certain degree of skin tightening. However, they may not be fully efficient. Therefore, post-bariatric patients with massive skin will require surgical treatment options.
Abdominoplasty procedures are the standard surgical treatment options for patients with massive skin in the abdomen and back after bariatric surgery. These procedures include:
Full Abdominoplasty
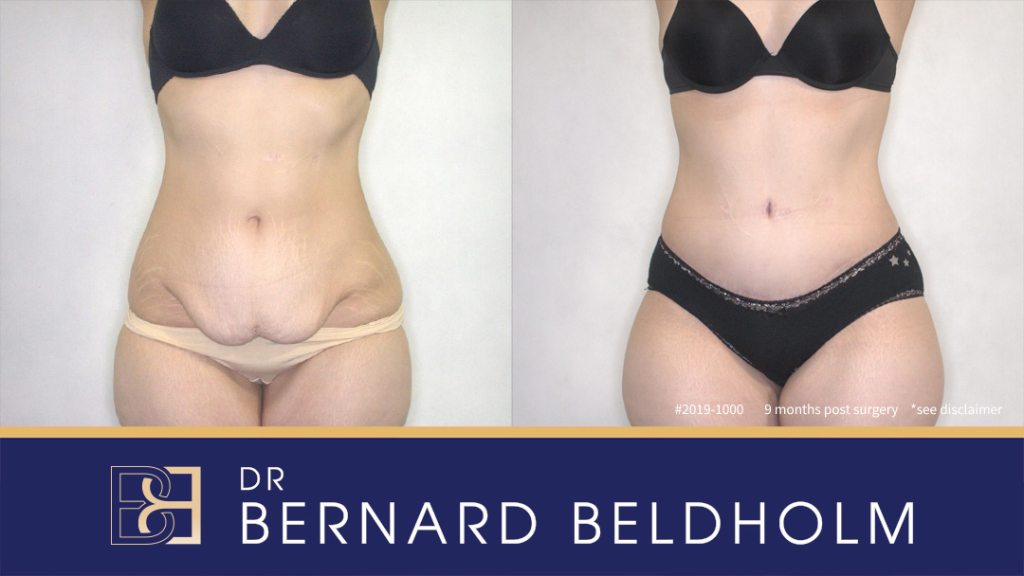
Full abdominoplasty post weight loss | BCSC
Disclaimer: Operation performed by Dr Bernard Beldholm. Adult content, surgery has risks; individual results vary, seek 2nd opinion. Please see the full disclaimer.
Full Abdominoplasty, also referred to as a complete/standard abdominoplasty, corrects diastasis recti (separated abdominal muscles), and repositions the belly button when required. The procedure is suitable for post-bariatric patients with loose skin in the lower and upper abdomen and minimal or no skin on the back.
A full abdominoplasty surgery takes 3-4 hours, and the patient spends 2-4 nights at the hospital for monitoring. Most full abdominoplasty patients can resume their daily activities 2-4 weeks after surgery.
Extended Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
Disclaimer: Operation performed by Dr Bernard Beldholm. Adult content, surgery has risks; individual results vary, seek 2nd opinion. Please see the full disclaimer.
Extended abdominoplasty also corrects diastasis recti and repositions the belly button. Suitable for post-bariatric patients with loose abdomen and back skin, extended abdominoplasty patients may require an intermediate procedure between a full abdominoplasty and belt lipectomy (circumferential abdominoplasty).
An extended abdominoplasty surgery has a longer surgery and recovery period than a full abdominoplasty. The surgery takes 4-5 hours, and patients can resume their daily chores within 3-6 weeks.
Fleur-de-Lis Abdominoplasty
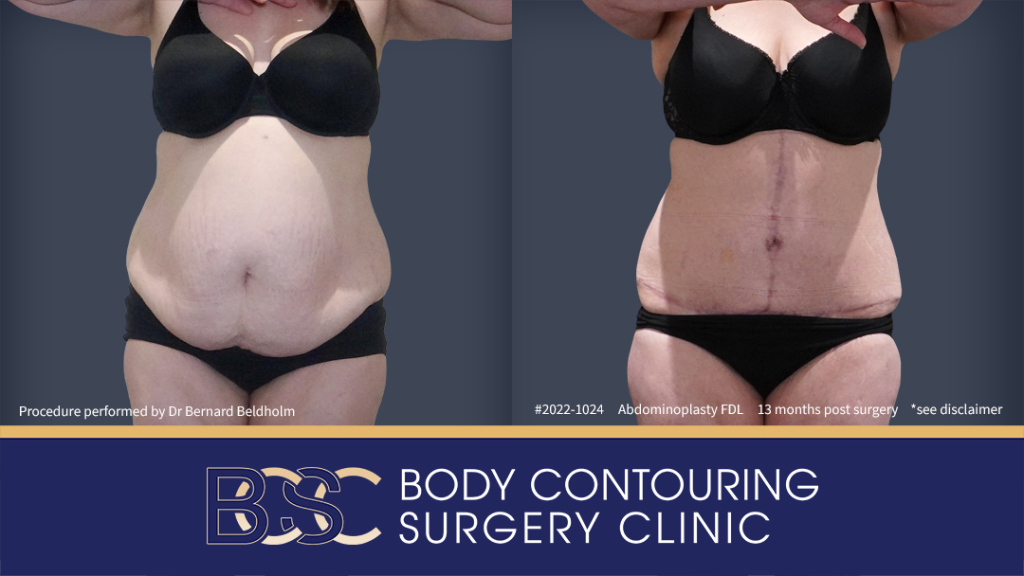
FDL Abdominoplasty Procedure performed by Dr. Bernard Beldholm, pictured, before and 13 months after surgery.
Disclaimer: Operation performed by Dr Bernard Beldholm. Adult content, surgery has risks; individual results vary, seek 2nd opinion. Please see the full disclaimer.
Fleur-de-Lis abdominoplasty is a common treatment for lax skin in major weight loss patients. It helps remove excess skin that would be challenging to eliminate with standard abdominoplasty procedures. The procedure involves an inverted T incision resembling a lily flower, hence its name.
Fleur-de-Lis abdominoplasty is suitable for major weight loss patients, bariatric surgery, and gastric bypass surgery patients with massive lax skin, especially in the upper abdomen. Despite its invasiveness, the procedure is not associated with increased complications. However, it has a longer surgery and recovery period.
A Fleur-de-lis abdominoplasty study on massive weight loss patients (50 pounds or more) concludes that “fleur-de-lis abdominoplasty can be performed with complication rates comparable to those of traditional abdominoplasty techniques.”
Abdominoplasty assisted by Suction-assisted lipectomy
Lipo-abdominoplasty is an abdominoplasty procedure that targets excess fat and loose abdominal skin by combining liposuction with abdominoplasty. The procedure involves removing excess fatty tissue through liposuction (Suction-assisted lipectomy) and then the excess skin through standard abdominoplasty procedures.
Lipo-abdominoplasty adds an additional hour to the time required for a standard abdominoplasty procedure.
“Lipo-abdominoplasty is a new, more physiological and versatile operation that drastically reduces complications, extends the indications for patient recruitment to the obese and super obese populations, and simplifies the surgery while also giving a better aesthetic result with ** recovery,” notes a study published in the National Library of Medicine.
VASER Liposuction (Suction-assisted lipectomy)
VASER (Vibration Amplification of Sound Energy at Resonance) liposuction uses ultrasound waves to liquefy fat deposits. The ultrasound liquefies the fat cells and separates the fatty tissue from the underlying muscle and skin. After liquefaction, the fat is removed through suction using cannulas.
Belt Lipectomy – Lower Body Lift Surgery
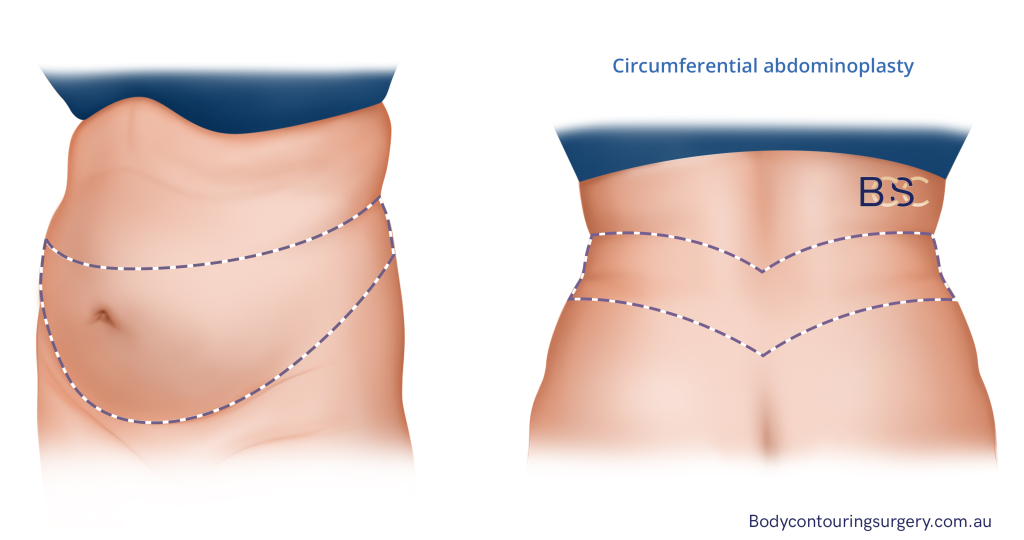
Body lift procedures to treat excess skin following gastric bypass surgery. Abdominoplasty Procedure performed by Dr. Bernard Beldholm, pictured, before and 13 months after surgery.
Belt Lipectomy, also known as a lower body lift surgery or circumferential abdominoplasty, is a common abdominoplasty procedure after major weight loss, removing loose skin 360 degrees around the “belt line”. The procedure removes excess skin on the abdomen, back, and buttocks and includes mons pubis and thigh.
Belt Lipectomy suits patients with “love handles” around the lower belly and back. In addition, the procedure targets loose skin on the thighs and buttocks.
Because the procedure covers a larger surgical area, it is more invasive than the other abdominoplasty procedures. Therefore, it requires more extensive surgery and a recovery period. The patient stays 5-7 days at the hospital after surgery and can resume their daily chores after 4-8 weeks.
Summary of Downtime and Recovery
Below is a breakdown of what to expect from the above surgical options.
- Full Abdominoplasty: Most patients can resume their daily activities after 2-4 weeks
- Extended Abdominoplasty: Patients can resume their daily activities after 3-6 weeks
- Belt Lipectomy (Circumferential Abdominoplasty): Patients can resume their daily activities after 4-8 weeks
- Full Vaser Lipo (Suction-assisted lipectomy) Abdominoplasty: Most patients can resume their daily activities after 2-4 weeks
- Extended Vaser Lipo (Suction-assisted lipectomy) Abdominoplasty: Patients can resume their daily activities after 2-4 weeks
Risks and Complications Associated with Surgical Treatment Options
Surgical treatments are characterised by an increased risk of complications when compared to non-surgical methods. In addition, abdominoplasty is associated with higher rates of complications than other aesthetic procedures, with the risk increasing with the procedure’s invasiveness.
A study on complication rates resulting from abdominoplasty notes that “[a]bdominoplasty is associated with a higher complication rate compared with other aesthetic procedures.” In addition, the study states that “[c]ombined procedures increased the risk of complication (abdominoplasty alone, 3.1 percent; with liposuction, 3.8 percent).”
The common complications resulting from surgical treatment options include:
- Haematoma
- Seroma
- Wound infections
- Skin necrosis
- Abnormal scarring
- Loss of skin sensitivity
- Blood clots
Cost Comparison of Surgical Treatment Options
The cost of each procedure mainly depends on its invasiveness, with more invasive procedures costing more. However, other factors like the patient’s needs, hospital location, and additional procedures like liposuction may affect the pricing.
Therefore, patients are advised to book a consultation with a specialist surgeon to customise the cost of their procedure.
Bottom Line
Most post-bariatric patients experience loose skin on the abdomen and back due to the massive weight loss resulting from the procedure. Therefore, most patients seek additional procedures to eliminate the excess abdominal and back skin. Non-invasive procedures like exercise, a healthy diet, topical treatments, cryotherapy, and lasers offer some degree of skin tightening. However, these procedures are not fully effective, requiring surgical treatment options like abdominoplasty procedures and liposuction (Suction-assisted lipectomy).
References
- Giordano, S., Victorzon, M., Koskivuo, I., & Suominen, E. (2013). Physical discomfort due to redundant skin in post-bariatric surgery patients. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 66(7), 950–955.
- Aldaqal, S. M., Makhdoum, A. M., Turki, A. M., Awan, B. A., Samargandi, O. A., & Jamjom, H. (2013). Post-bariatric surgery satisfaction and body-contouring consideration after massive weight loss. North American journal of medical sciences, 5(4), 301–305.
- Elander, A., Biörserud, C., & Fagevik Olsén, M. (2021). Excess skin after weight loss following bariatric surgery: focus on the abdomen. Surgery for obesity and related diseases : official journal of the American Society for Bariatric Surgery, 17(5), 986–993.
- Sadeghi, P., Duarte-Bateman, D., Ma, W., Khalaf, R., Fodor, R., Pieretti, G., Ciccarelli, F., Harandi, H., & Cuomo, R. (2022). Post-Bariatric Plastic Surgery: Abdominoplasty, the State of the Art in Body Contouring. Journal of clinical medicine, 11(15), 4315.
- de Souza Pinto, E. B., Abdala, P. C., Maciel, C. M., dos Santos, F.deP., & de Souza, R. P. (2006). Liposuction and VASER. Clinics in plastic surgery, 33(1), 107–vii.
- Hoyos, A. E., & Millard, J. A. (2007). VASER-assisted high-definition liposculpture. Aesthetic surgery journal, 27(6), 594–604.
- Rangaswamy M. (2008). Lipoabdominoplasty: A versatile and safe technique for abdominal contouring. Indian journal of plastic surgery : official publication of the Association of Plastic Surgeons of India, 41(Suppl), S48–S55.
- Friedman, T., O’Brien Coon, D., Michaels V, J., Purnell, C., Hur, S., Harris, D. N., & Rubin, J. P. (2010). Fleur-de-Lis abdominoplasty: a safe alternative to traditional abdominoplasty for the massive weight loss patient. Plastic and reconstructive surgery, 125(5), 1525–1535.
- Aly, A. S., Cram, A. E., Chao, M., Pang, J., & McKeon, M. (2003). Belt lipectomy for circumferential truncal excess: the University of Iowa experience. Plastic and reconstructive surgery, 111(1), 398–413.
- Winocour, J., Gupta, V., Ramirez, J. R., Shack, R. B., Grotting, J. C., & Higdon, K. K. (2015). Abdominoplasty: Risk Factors, Complication Rates, and Safety of Combined Procedures. Plastic and reconstructive surgery, 136(5), 597e–606e.
Disclaimer: ADULT content. Dr Bernard Beldholm is a Specialist General Surgeon (AHPRA Medical Registration nr: MED0001186274). Any surgical or invasive procedure carries risks. Before proceeding, you should seek a second opinion from a qualified health practitioner. Results, recovery & potential complications will vary for each individual patient. Photos & videos featured are not a guarantee that your results will be the same & do not guarantee a particular surgical outcome. Content on our Instagram page & other social media pages is published with the consent of our patients. The content featured is general in nature and does not constitute medical advice. Immediate post-op results may differ from the final result.