How Much Does an Abdominoplasty Cost in Australia 2024?
One of the greatest factors patients must consider when contemplating abdominoplasty surgery is cost.
Abdominoplasty surgery is a procedure designed to remove excess skin and fat in the abdomen, upgrade abdominal contour, and repair separated abdominal wall muscles. It is among the most popular cosmetic surgery procedures in Australia. Despite this, the issue of the cost of an abdominoplasty remains a major concern.

Average Price of an Abdominoplasty in Australia
The average cost of an abdominoplasty in Australia in 2024 ranges from $10,000 to $30,000. This is an estimated price, however, and may vary significantly among patients. For this reason, each patient will get a personalised quotation from their surgeon who will take the patient’s specific goals and needs when designing a customised surgical plan.
What the Cost of Abdominoplasty Normally Includes
The cost of an abdominoplasty includes the following:
- Surgeon’s fee (depending on the provider, this may or may not include aftercare.)
- Anaesthetic fee and anaesthestetist’s fees
- Surgical room fee
- Hospital fee (for procedures requiring hospital stay)
- Medications and prescriptions
Note: As the price quotation might not cover extra costs for surgical garments like compression bras, and scar treatments, so it’s important for patients to request a clarification of what the quoted price covers and what is not covered prior to scheduling surgery.
Factors Determining Cost of Abdominoplasty Surgery
- Type of procedure (Full, Mini, or Extended (Fleur de Lis)
- Reason for procedure (medical or cosmetic)
- Whether liposuction is included
- Size of patient
- Whether there is MBS item number or not
- Whether procedure is covered by Medicare or other health insurance
- Surgeon’s experience
- Hospital Fees
- Anaesthetic and aenesthestetist’s fees.
- Location
- Other fees
As the cost of an abdominoplasty depends on several factors, it’s important for patients to understand each one.
Type of Abdominoplasty Procedure
Different abdominoplasty surgical procedures have different prices due to differences in invasiveness, surgical duration, and hospital stay. The price of a procedure will also increase if liposuction is involved. Below are the different abdominoplasty procedures and their costs.
Mini Abdominoplasty
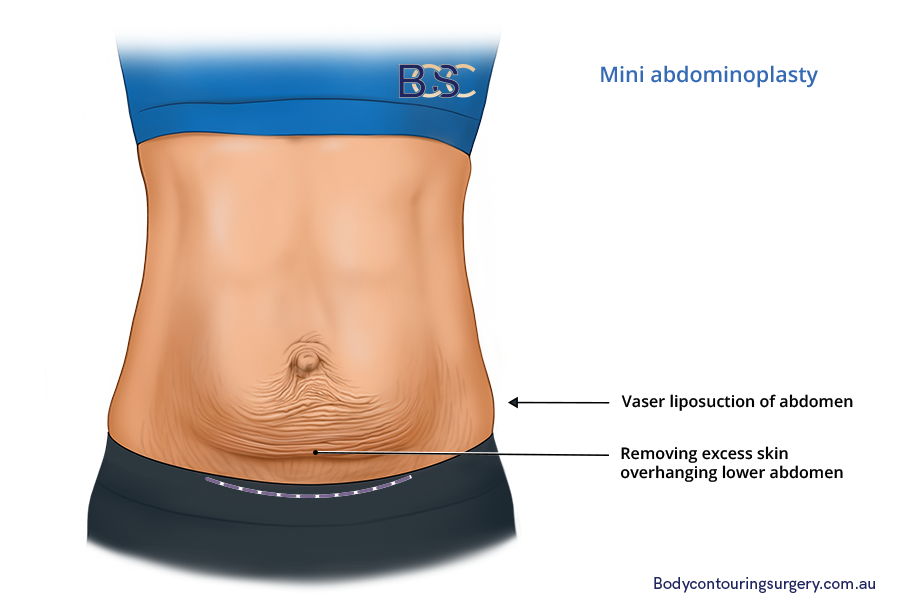
Mini Abdominiplasty | BCSC
A mini abdominoplasty involves removing excess skin and fat in the lower abdomen without umbilicus repositioning. It is less invasive than other types of abdominoplasty procedures, and you can go home on the day of the surgery.
Mini Abdominoplasty Without Liposuction
A mini abdominoplasty without liposuction takes approximately 1 hour. Below is a breakdown of the expected cost.
- Hospital Fee: $2000-5000
- Surgeon Fes: $3000-6000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $1200-3000
Mini Abdominoplasty With Liposuction
On the other hand, a mini abdominoplasty with liposuction takes a longer period, usually an additional 1 hour. The charges include,
- Hospital Fee: $4000-7000
- Surgeon Fee: $4000-8000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $2000-4000
Full Abdominoplasty
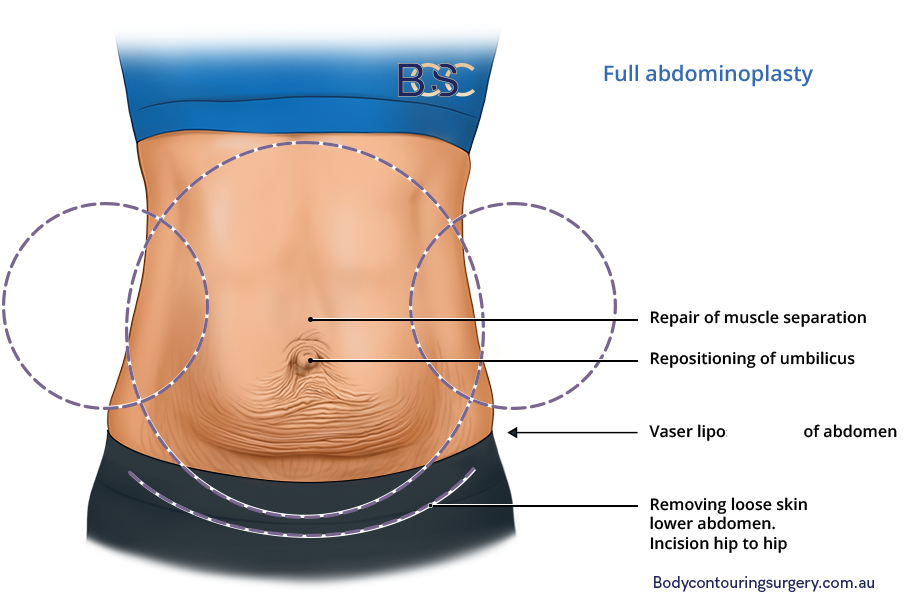
A full abdominoplasty is more invasive than a mini abdominoplasty. The procedure removes loose skin and fat in the entire abdomen (lower and upper), separated abdominal muscles (diastasis recti), and repositions the umbilicus. A full abdominoplasty can be cosmetic or reconstructive, with a MBS item number.
Full Abdominoplasty Without Liposuction
A full abdominoplasty without liposuction takes approximately 2.5 hours and one to three hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon Fee: $6000-12000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $3000-5000
- Hospital Fee: $6000-10000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)
Full Abdominoplasty With Liposuction
A full abdominoplasty with liposuction takes around four hours and one to three hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon fee $8000-14000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $3000-7000
- Hospital Fee: $8000-15000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)
Extended Abdominoplasty
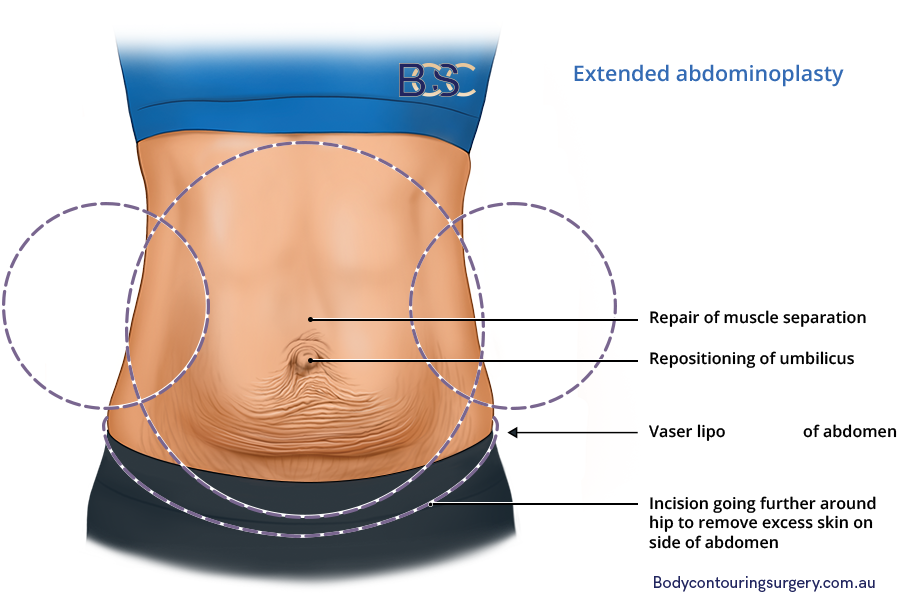
This procedure is more invasive than a full abdominoplasty, removing excess abdominal skin and fat in the abdomen, hip, and back region.
Extended Abdominoplasty Without Liposuction
An extended Abdominoplasty without liposuction takes around three hours and requires one to three hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon Fee: $6000-12000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $3000-5000
- Hospital Fee: $6000-11000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)
Extended Abdominoplasty With Liposuction
An extended abdominoplasty with liposuction takes around five hours and requires two to four hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon Fee: $8000-14000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $3000-7000
- Hospital Fee: $8000-17000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)
Circumferential Abdominoplasty (Belt Lipectomy)
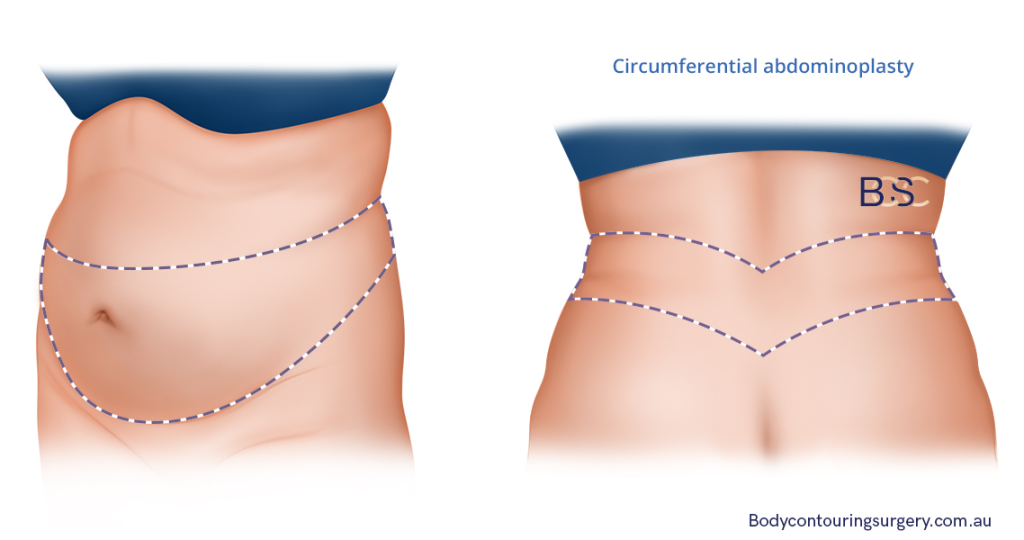
A circumferential abdominoplasty, also known as a body lift, involves excess skin and fat removal in the tummy, back, hips, and buttocks. It’s extensive, with an incision creating a complete circle around the tummy.
Circumferential Abdominoplasty Without Liposuction
A circumferential abdominoplasty without liposuction takes around five hours and three to five hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon Fee: $12000-24000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $4000-9000
- Hospital Fee: $10000-20000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)
Circumferential Abdominoplasty Without Liposuction
A circumferential abdominoplasty with liposuction takes around seven hours and three to five hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon Fee: $15-26000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $5000-12000
- Hospital Fee: $14000-25000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)
Reverse Abdominoplasty
Unlike most abdominoplasties, a reverse abdominoplasty targets the upper abdomen. It involves excess skin removal on the area above the belly button and tightening the upper abdominal muscles. A reverse Abdominoplasty incision runs along the bra line. It’s suitable for patients undergoing a mastopexy (breast lift).
Reverse Abdominoplasty Without Liposuction
A reverse abdominoplasty without liposuction takes approximately 2.5 hours and one to three hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon Fee: $6000-12000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $3000-5000
- Hospital Fee: $6000-10000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)
Reverse Abdominoplasty With Liposuction
A reverse abdominoplasty with liposuction takes around four hours and one to three hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon fee $8000-14000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $3000-7000
- Hospital Fee: $8000-15000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)
Fleur De Lis (FDL) Abdominoplasty
Fleur De Lis Abdominoplasty, also known as a vertical abdominoplasty, involves a full belt incision across the waist and an additional vertical incision in the front. The procedure is very invasive and involves greater costs.
Fleur De Lis (FDL) Abdominoplasty Without Liposuction
A Fleur De Lis (FDL) Abdominoplasty without liposuction takes around three hours and requires one to three hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon Fee: $6000-12000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $3000-5000
- Hospital Fee: $6000-11000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)
Fleur De Lis (FDL) Abdominoplasty With Liposuction
A Fleur De Lis (FDL) Abdominoplasty with liposuction takes around five hours and requires two to four hospital days. The charges include:
- Surgeon Fee: $8000-14000
- Anaesthetic Fee: $3000-7000
- Hospital Fee: $8000-17000 (excluded if you have Medicare or private insurance coverage)

Reason for Abdominoplasty
Is the abdominoplasty a cosmetic surgery, or is it a reconstructive surgery? Cosmetic procedures are more expensive than reconstructive procedures. Reconstructive procedures may also attract Medicare rebates if you qualify for a MBS Item Number, making them cheaper.
In addition, the reason for an abdominoplasty determines whether the cost will include a GST (Goods and Service Tax). GST is a 10% tax on goods and services consumed or sold in Australia.
Medicare is exempt from GST, meaning that if you qualify for an MBS Item Number, your procedure is considered medical and is exempt from GST. However, if you do not qualify for an MBS Item Number, your procedure is considered cosmetic, meaning that GST applies to the cost of the procedure. Therefore, the same procedure becomes 10% more expensive.
Medicare Coverage (MBS Item Number)

Medicare coverage is a crucial determiner of the cost of an abdominoplasty. Medicare does not cover cosmetic surgical procedures. However, Medicare only covers an abdominoplasty if it’s deemed medically necessary.
There are two groups of patients that qualify for a MBS item number.
- Post-weight loss patients
- Post-pregnancy patients with at least 3 cm of separation that is causing medical issues
Post pregnancy patients qualify for MBS Item Number 30175. To be eligible, you must demonstrate “diastasis recti of at least 3 cm, have moderate discomfort and pain at the site of diastasis, prove failure of non-surgical treatment methods, and not have been pregnant for at least 12 months.” Note that Medicare doesn’t offer rebates to women whose primary goal for an abdominoplasty is to get rid of excess post-pregnancy skin.
On the other hand, Post weight loss patients qualify for MBS Item Number 30177. For eligibility, you must demonstrate “at least 5 BMI weight loss, stable weight for at least 6 months after the significant weight loss, excess skin affecting your normal activities, and intertrigo or other skin infection that’s affecting the skin integrity.”
If you are eligible and qualify for a Medicare Benefits Schedule (MBS) Item Number, Medicare will cover a portion of the procedure’s cost. In addition, patients with a MBS item number do not pay for the hospital (which is one of the most expensive parts $8-18,000).
Private Health Insurance
Private health funds don’t cover cosmetic abdominoplasty, covering only medical procedures (you will get covered if you have an MBS item number). However, you must have the correct level of coverage, usually the top level (Gold level). The health fund may also cover your hospital stay and a portion of the surgeon’s and anaesthetic charges.
Patients with an MBS item number and qualify for private health insurance coverage do not pay for the hospital, and they also get the rebate back from health funds. Note that you will still pay some amount out of pocket. This is known as a GAP, a payment you pay out-of-pocket when the treatment cost is higher than the amount you claim from your insurance.
Duration of the Procedure
Hospitals/ surgeons/ anaesthetic costs are usually calculated depending on the time the procedure takes. The longer an abdominoplasty takes, the higher the abdominoplasty prices. For instance, mini abdominoplasty takes 1 hour, full abdominoplasty takes 4 hours, and extended abdominoplasty surgery takes 5 to 6 hours. The longer it takes the more expensive the surgery will be.
The type of abdominoplasty and the procedure’s complexity determine the duration. More complex procedures will require more extended periods than less complicated procedures. The complexity of a procedure depends on whether the abdominoplasty treats one or a combination of the following factors:
- Removal of excess abdominal fat and skin and the extent of removal
- Repair of abdominal muscles (Diastasis recti)
- Hernia repair
- Liposuction (suction-assisted lipectomy)
Surgeon’s Experience
Highly skilled and experienced surgeons charge more for their services because of their high demand and high-level care. Most surgeons calculate their price based on the procedure’s duration and complexity. In addition, the price will also reflect the surgeon’s qualifications, popularity, and professional recognition. The surgeon’s fee may include an initial consultation fee, or the surgeon may quote it separately.
However, a high surgeon’s fee does not always guarantee expertise. Therefore, research before settling for a surgeon purely based on the pricing. Also, discounted or low prices may signal that the surgeon is inexperienced. This may not always be the case, but it’s important not to sacrifice quality for lower prices.
Hospital Fees
You can undergo an abdominoplasty in a private overnight hospital or a day procedure hospital. However, an abdominoplasty is not suitable in a day procedure hospital unless it’s a mini abdominoplasty.
Private hospitals set their fees and the cost will vary. However, the hospital fees mainly depend on the expected surgery time. Therefore, the hospital fees will increase if the procedure takes a long period.
The other cost affecting the hospital fees is the duration spent in the hospital after surgery. The hospital fee is usually $1200-2400 per day, depending on the hospital. Complex procedures require more hospital stays and thus cost more. Note that patients don’t pay the hospital fee if they have an MBS item number and private health insurance coverage.
Anaesthesia Fees
The surgeon can use either general or local anaesthesia during an abdominoplasty. The type of anaesthesia mostly depends on the procedure’s extensiveness. General anaesthesia is more expensive than local anaesthesia. In addition, the anaesthesia fee will depend on the experience and qualifications of the anaesthetic.
Ideally, these vary from $500-700 per hour and the anaesthetist will charge 1-2 hours more than the surgical time. For instance, if the surgical time is 4 hours the anaesthetist may charge for 6 hours.
Location
The geographical location where you undergo an abdominoplasty will affect the procedure’s cost. This may result from factors like the cost of living in the area. Therefore, surgeons located in metropolitan states are likely to charge higher than those in smaller cities.
Pre-operative Tests
Pre-operative tests are essential before an abdominoplasty since they help determine the expected complications or care needed. These tests, like the ECG or blood work, may increase the procedure’s cost.
Other costs
The price quotation may not include some costs like post-operative care, surgical garments, and medication, among others. Additional of these extra costs will affect the overall price of an abdominoplasty. Therefore, you must know what extra abdominoplasty prices you will incur before surgery.
However, at Body Contouring and Surgery Clinic, all your aftercare is included in the price. This includes the garments, follow-up care, dressings, etc.
Bottom Line
The cost of an abdominoplasty will differ for every patient. This is because the cost varies depending on the surgeon’s experience and expertise, location, hospital fees, anaesthetic fees, type of abdominoplasty, and the patient’s general health. Therefore, the best solution is to consult a qualified specialist surgeon for a customised price quotation. Ensure you choose the right specialist surgeon for your abdominoplasty.
References
- Michalska, A., Rokitaⴕ, W., Wolder, D., Pogorzelska, J., & Kaczmarczyk, K. (2018). Diastasis recti abdominis — a review of treatment methods. Ginekologia Polska, 89(2), 97–101.
- Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing. (n.d.). MBS Online – MBS Online.
- Greminger, R. F. (1987). The Mini-Abdominoplasty. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 79(3), 356–364.
- Dini, M., Mori, A., Cassi, L. C., Russo, G., & Lucchese, M. (2008). Circumferential abdominoplasty. Obesity Surgery, 18(11), 1392–1399.
- Whalen, K. S., Liu, L., Rejano, C. J., Mhaskar, R., Khakpour, N., & Dayıcıoğlu, D. (2023). Reverse abdominoplasty for mastectomy defect closure in advanced breast cancer. Annals of Plastic Surgery, 90(3), 204–208.
- Shestak, K. C. (2014). The extended abdominoplasty. Clinics in Plastic Surgery, 41(4), 705–713.
- Dellon, A. L. (1985). Fleur-de-lis abdominoplasty. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 9(1), 27–32.
- Brauman, D., & Capocci, J. (2009). Liposuction abdominoplasty: an advanced body contouring technique. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 124(5), 1685–1695.
- Staalesen, T., Elander, A., & Strandell, A. (2012). A systematic review of outcomes of abdominoplasty. Journal of Plastic Surgery and Hand Surgery, 46(3–4), 139–144.


