Abdominoplasty After Weight Loss
Abdominoplasty targets excess skin and tissue in the abdominal area after significant weight loss. It offers a solution by removing excess skin and fat, tightening the abdominal muscles (diastasis recti), and creating a smoother abdomen.
In recent years, abdominoplasty has gained popularity in Australia. As per the latest studies, the number of women undergoing this procedure has risen substantially, with a report indicating an increase of over 30% in the past decade alone.
Weight loss can result from dieting, exercising, or bariatric surgery. Weight loss can lead to discomfort, functional limitations, excess skin, and muscle weakening or separation (diastasis recti). Today, we will explore abdominoplasty after weight loss, covering indications, surgical techniques, risks, and more.
Reasons to Consider Abdominoplasty After Weight Loss
When a person gains weight, their skin stretches to accommodate the increased volume of fat cells. Additionally, the abdominal muscles weaken, and stretch marks form. The increase of fat in the intra-abdominal area leads to muscle separation (diastasis recti) in the midline. This can be pronounced especially for women after pregnancy.
When a person loses weight, it decreases the amount of fat in the body. This is especially true within the subcutaneous layer. The person might still experience stretched skin even after their weight loss journey. This can result in loose skin and tissue that may hang down over the waistline, creating an appearance commonly referred to as an “apron” or “pannus.” This excess skin can cause discomfort and hinder physical activity.
Significant weight loss also contributes to weakened abdominal muscles and poor core strength. It is difficult to perform everyday tasks that require core stability, such as bending, lifting, and twisting, with weakened abdominal muscles.
Abdominoplasty targets this issue by incorporating a procedure called plication (diastasis recti repair) during the surgery. Plication involves suturing the weakened or separated abdominal muscles, tightening them to create a firmer and more toned abdominal wall.
Surgical Techniques Abdominoplasty After Weight Loss
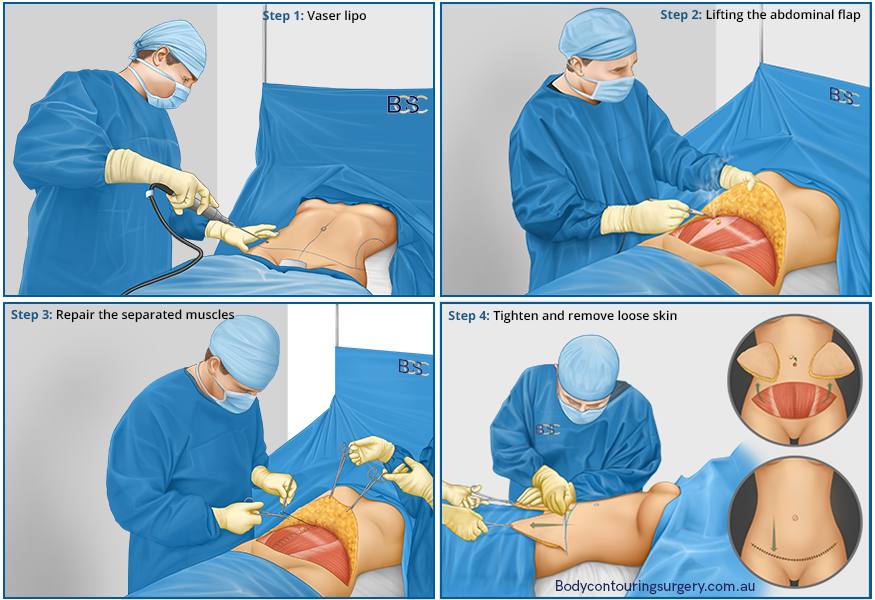
Abdominoplasty surgery technique | BCSC
Surgeons use several surgical techniques for abdominoplasty after weight loss. The ideal technique depends on the patient’s anatomy, goals, and the extent of excess skin tissue. Standard surgical methods are:
Full Abdominoplasty
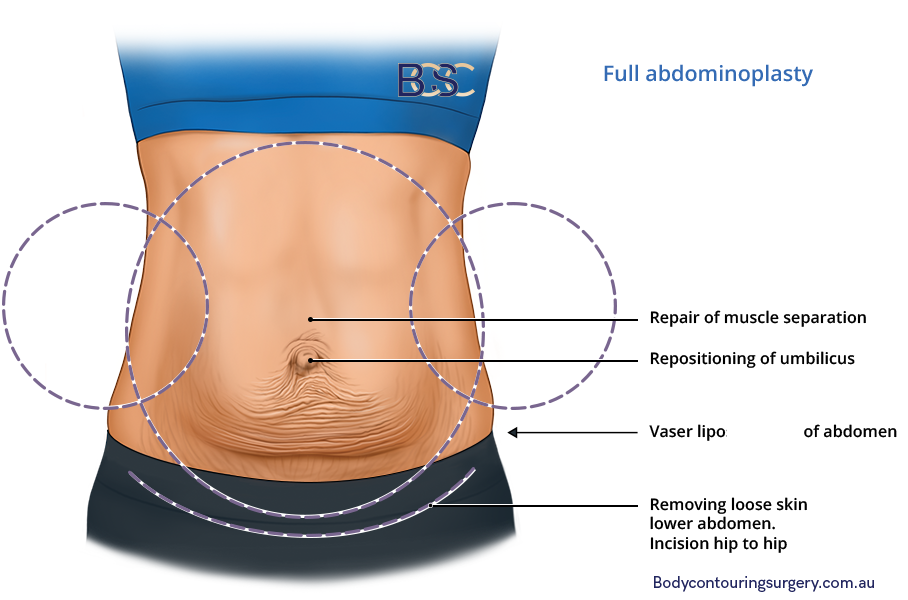
Full abdominoplasty | BCSC
This procedure involves a horizontal incision, which is made above the pubic area and extends from hip to hip. The surgeon then lifts the skin and tightens the underlying muscles. If necessary, he removes excess skin and fat and re-drapes the remaining skin. This procedure will suit patients with excess skin and tissue in the abdominal area. Studies have reported high success rates for this technique, with rates exceeding 90% in many cases.
Extended Abdominoplasty
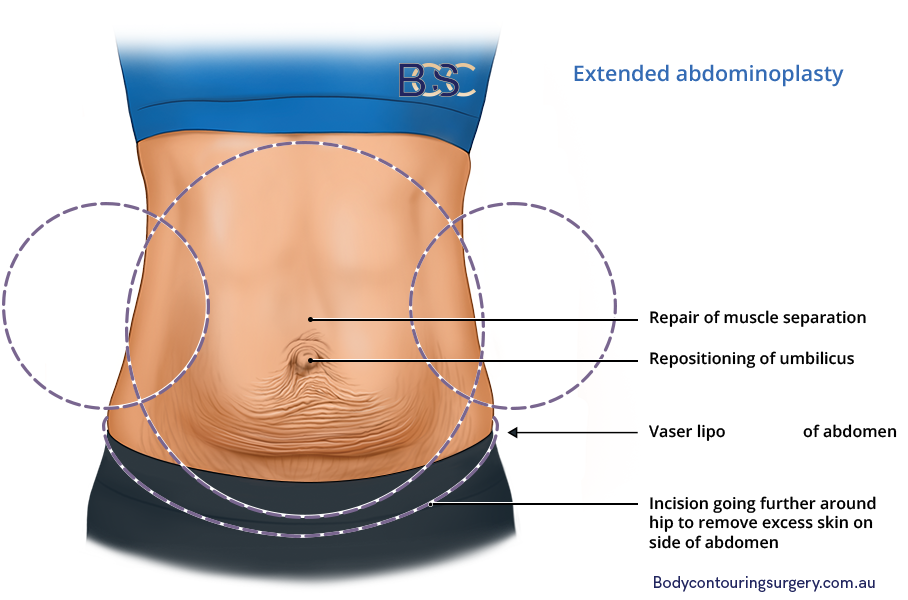
Extended abdominoplasty | BCSC
The procedure involves a longer incision beyond the hips. It removes excess skin and tissue on the sides of the abdomen and the lower back. This procedure suits patients with significant excess skin and tissue in the front and sides of the abdomen.
Mini Abdominoplasty
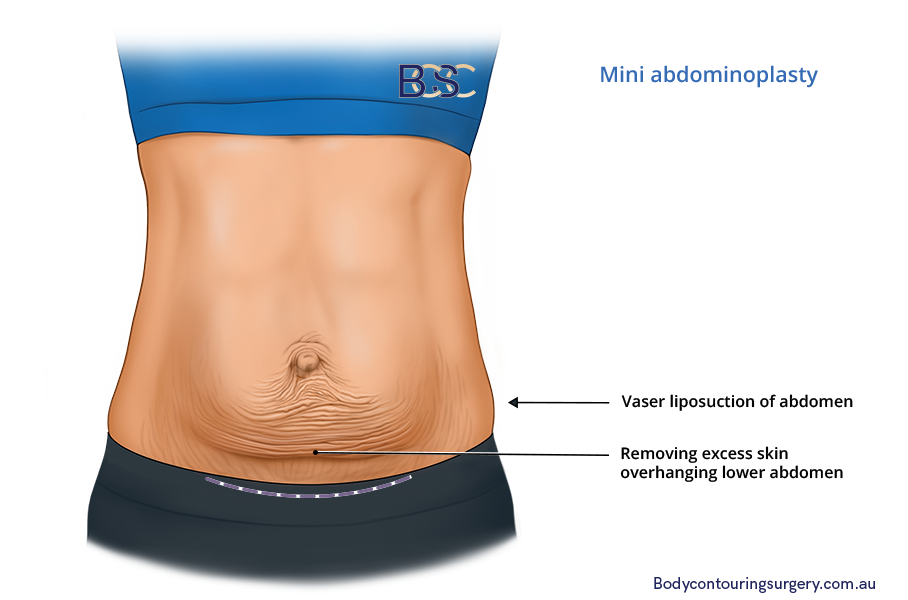
Mini abdominoplasty | BCSC
Mini abdominoplasty is a less invasive variation of the full abdominoplasty. The smaller incision primarily targets excess skin and tissue on the lower abdomen below the navel. This procedure suits people with mild to moderate excess skin and tissue in the lower abdominal region.
Reverse Abdominoplasty
In this technique, the incision is made on the upper abdomen, usually below the breasts. Surgeons use this technique less frequently and primarily in patients with excess skin and tissue in the upper abdomen.
Fleur-de-lis Abdominoplasty
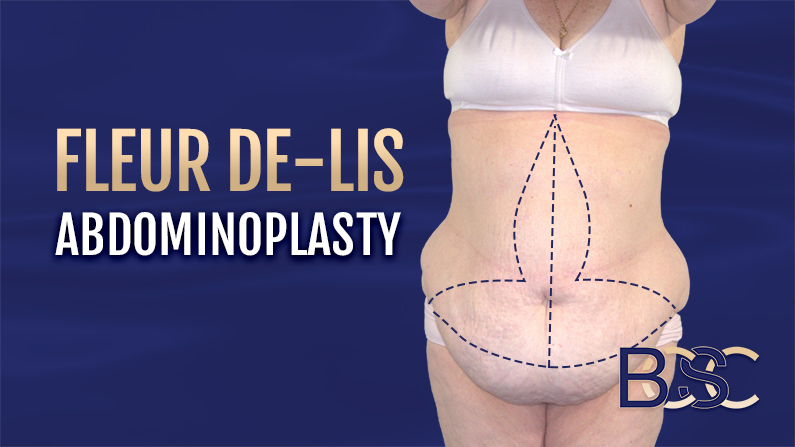
Abdominoplasty surgeons use this technique when there is excess skin and tissue horizontally and vertically. It involves a vertical incision along the midline of the abdomen, resulting in a scar that resembles a “fleur-de-lis” shape. This technique allows for more extensive removal of excess skin and tissue and may be suitable for patients with massive weight loss or significant abdominal laxity.
While fleur-de-lis abdominoplasty offers significant benefits in abdominal contouring, patients must understand that it typically results in more extensive scarring than traditional or standard abdominoplasty. However, many patients find that the abdominal appearance outweighs concerns about scarring. Ideally, these scars tend to fade over the years.
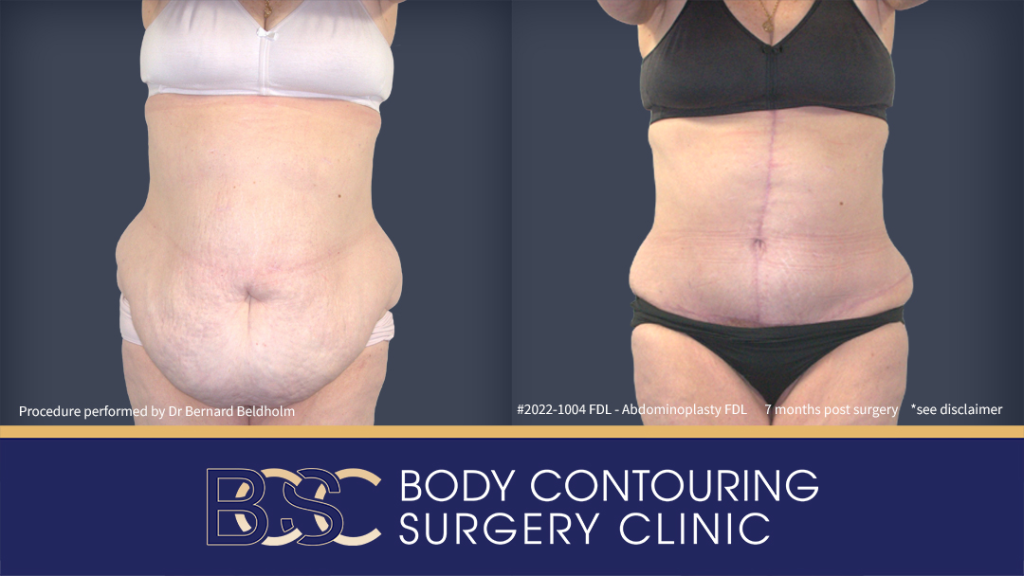
Fleur de lis abdominoplasty Before & After performed by Dr Beldholm
Recovery Process of Abdominoplasty After Weight Loss
Every patient’s recovery process differs depending on individual factors, like the extent of surgery and the patient’s overall health. Below is an overview of the general recovery process after abdominoplasty for weight loss:
Immediate Postoperative Period (Days 1-3)
Immediately after the surgery, the patient is admitted to the hospital for close supervision for pain management and to ensure they recover well. As needed, healthcare professionals administer antibiotics and pain medication to control discomfort.
The First Few Weeks
After discharge from the hospital, the patient is given instructions for postoperative care and follow-up appointments. It is essential to adhere to activity restrictions, including avoiding strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and bending at the waist, to prevent complications and promote proper healing.
Midterm Recovery (weeks 2-4) Postoperative
Swelling and bruising should gradually subside during this period. Patients may begin to see initial changes in abdominal contour. Dr. Beldholm encourages all his patients to continue wearing compression garments as instructed and to follow any additional postoperative care recommendations. This will keep the recovery moving forward smoothly.
Months (1-3)
By this time, most of the swelling has resolved.
Long-term recovery (months 3 and beyond)
Full recovery from abdominoplasty after weight loss may take several months, and final results may continue to change for the better over a year or more. One should maintain a healthy lifestyle, which includes regular exercise and a balanced diet to optimise and sustain abdominoplasty results.
As all patients are different, the healing process can vary from one person to another.
Throughout the recovery process, patients are required to adhere to their surgeon’s postoperative instructions, attend the scheduled follow-up appointments, and communicate with their specialist surgeon should any problem arise. By adhering to these guidelines and allowing adequate time for healing, patients can achieve optimal results and enjoy the benefits of abdominoplasty after weight loss.
Outcomes Of Abdominoplasty After Weight Loss
Further examination of patient-reported outcomes reveals the multifaceted benefits of abdominoplasty after weight loss. Studies have shown that patients often experience positive results in various aspects beyond physical appearance.
Physically, patients typically experience a smoother and firmer abdomen, leading to reduced skin irritation and posture. Abdominoplasty after weight loss can also help abdominal function. The procedure can also help core strength and stability by tightening the abdominal muscles and removing excess skin and fat, leading to better support for the spine and pelvis.
Risks and Complications Associated With Abdominoplasty
Just like any other medical procedure, abdominoplasty after weight loss carries certain risks and potential complications. While most patients undergo abdominoplasty without experiencing significant issues, it is essential to be aware of the potential dangers, which may include:
- Bleeding – Bleeding may occur during the surgery or the postoperative period. While the surgeon typically controls some bleeding during surgery, excessive bleeding can lead to the formation of a hematoma.
- Haematoma – Haematoma is a collection of blood that pools under the skin at the surgical site. It appears swollen and bruised and may cause discomfort or pain. Hematomas can vary in size and severity.
- Seroma formation – Fluid accumulation under the skin, known as seroma, can occur after surgery and may require aspiration or drainage to prevent further complications.
- Infection – There is a risk of infection at the surgical site, manifesting as redness, swelling, or warmth. General specialist surgeons may prescribe antibiotics to treat or prevent disease. Statistics indicate that infection rates range from 2-4%, emphasising the importance of diligent postoperative care.
Following the surgeon’s preoperative and postoperative instructions is essential since it can minimise the risk of complications and promote optimal recovery.
What to Consider Before Undergoing an Abdominoplasty Surgery Following Weight-Loss
Before undergoing abdominoplasty surgery following massive weight loss, several essential factors must be considered to ensure the best possible outcome and experience.
Sufficient Knowledge of Abdominoplasty
Before you decide to have an abdominoplasty surgery after weight loss, it is vital to know everything that comes with it. This includes the surgery requirement, benefits, and risks. It is advisable to schedule a consultation with a FRACS specialist surgeon to learn more about this journey.
Overall Health and Fitness
It is essential to be in good health before undergoing abdominoplasty surgery. Patients should have stable weight, well-controlled medical conditions, and no active infections. Patients should undergo a thorough physical exam to ensure that they are fully fit for surgery.
Recovery and Downtime
Recovery from abdominoplasty surgery typically involves rest and limited activity to allow the body to heal correctly. It is essential to plan for this downtime and arrange for help with daily tasks as needed during recovery. Every person is unique, and so are our bodies. The healing process may vary from one patient to another. If you are planning to get pregnant, for example, discuss this with your surgeon at your consultation.
Realistic Expectations
While abdominoplasty can significantly upgrade the abdomen’s appearance by removing excess skin and tissue, it is crucial to understand that it is not a substitute for weight loss. Patients should always discuss their goals and expectations with their surgeon for clarity.
If you are considering abdominoplasty after weight loss, take the first step toward achieving your goals by scheduling a consultation with Dr. Bernard Beldholm. With his expertise and personalised approach, Dr. Beldholm can guide you through the process, discuss potential outcomes, and answer any questions you may have.
References
- Jacobs, J. B., Schechner, S., & Jacobs, J. S. (2006). Abdominoplasty following massive weight loss. Seminars in Plastic Surgery, 20(01), 015–023.
- Brower, J. P., & Rubin, J. P. (2020). Abdominoplasty after massive weight loss. Clinics in Plastic Surgery, 47(3), 389–396.
- Restifo, R. J. (2021). Abdominoplasty in the massive weight loss patient: Are aesthetic goals and safety mutually exclusive? Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 3(2).
- Stuerz, K., Piza, H., & Kinzl, J. F. (2013). The impact of abdominoplasty after massive weight loss. Annals of Plastic Surgery, 71(5), 547–549.
- Hodgkinson, E. L., Smith, D., & Wittkowski, A. (2014). Women’s experiences of their pregnancy and postpartum body image: a systematic review and meta-synthesis. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, 14(1).
- Cannistrà, C., Lori, E., Arapis, K., Gallo, G., Varanese, M., Pironi, D., De Luca, A., Frusone, F., Amabile, M. I., Sorrenti, S., Gagliardi, F., & Tripodi, D. (2024). Abdominoplasty after massive weight loss. Safety preservation fascia technique and clinical outcomes in a large single series-comparative study. Frontiers in Surgery, 11.
- Stuerz, K., Piza, H., & Kinzl, J. F. (2013b). The impact of abdominoplasty after massive weight loss. Annals of Plastic Surgery, 71(5), 547–549.
- Hunecke, P., Toll, M., Mann, O., Izbicki, J. R., Blessmann, M., & Grupp, K. (2019). Clinical outcome of patients undergoing abdominoplasty after massive weight loss. Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases, 15(8), 1362-1366.
- Hurvitz, K. A., Olaya, W., Nguyen, A., & Wells, J. H. (2014). Evidence-Based medicine. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 133(5), 1214–1221.